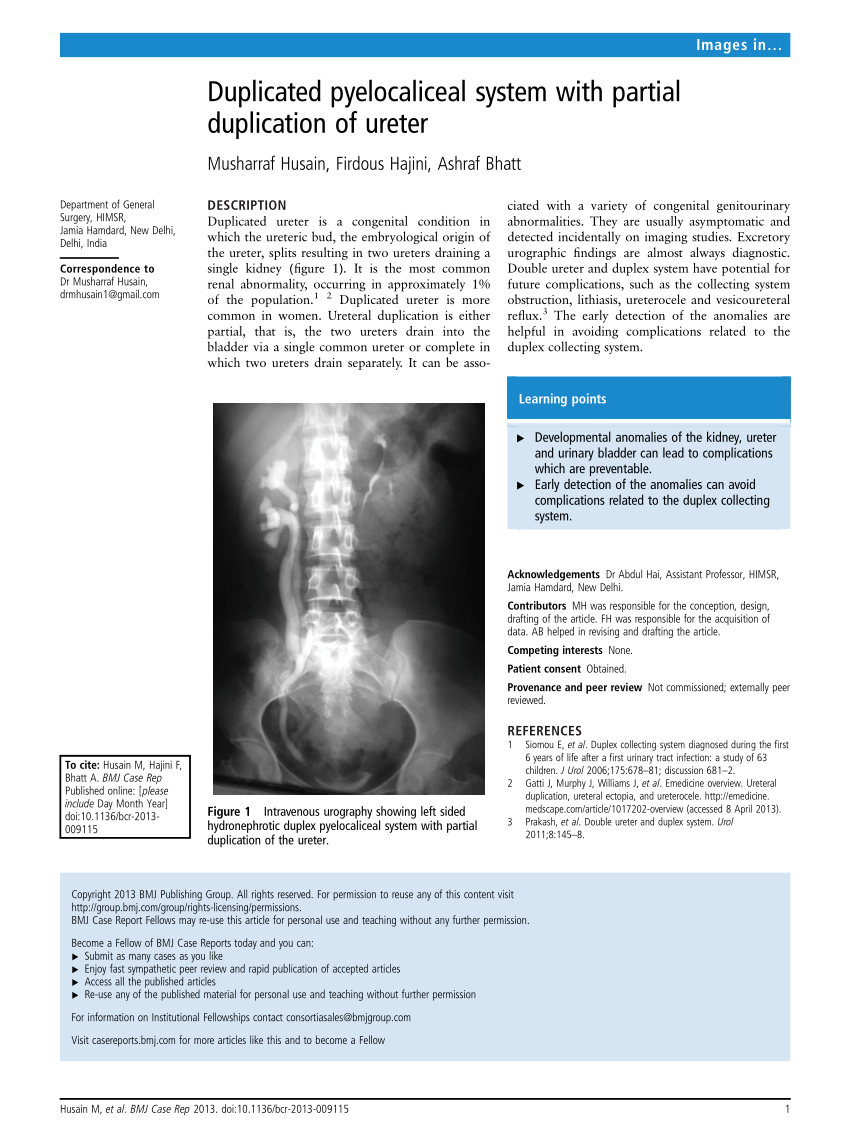
Duplicated Left Renal Collecting System
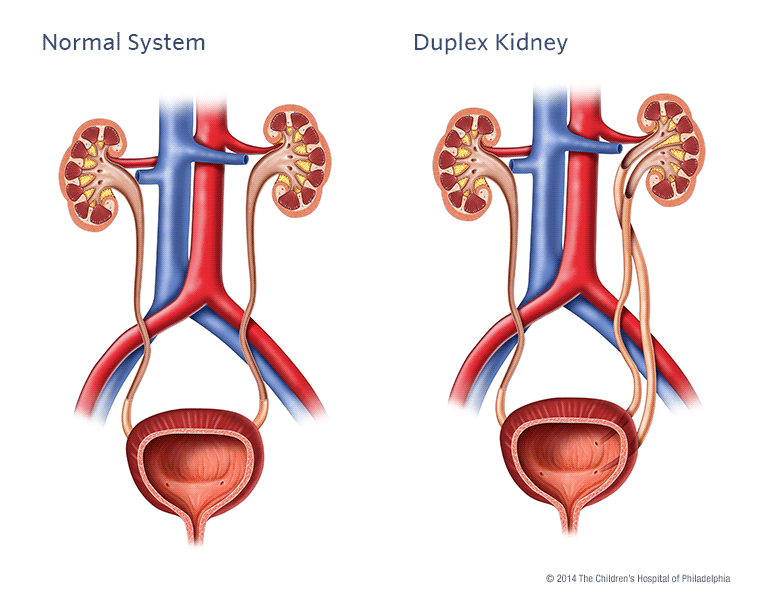
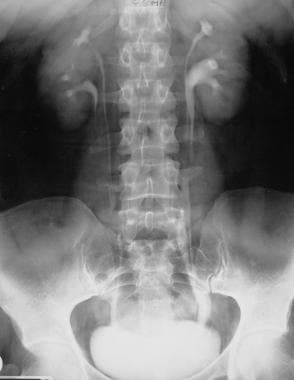
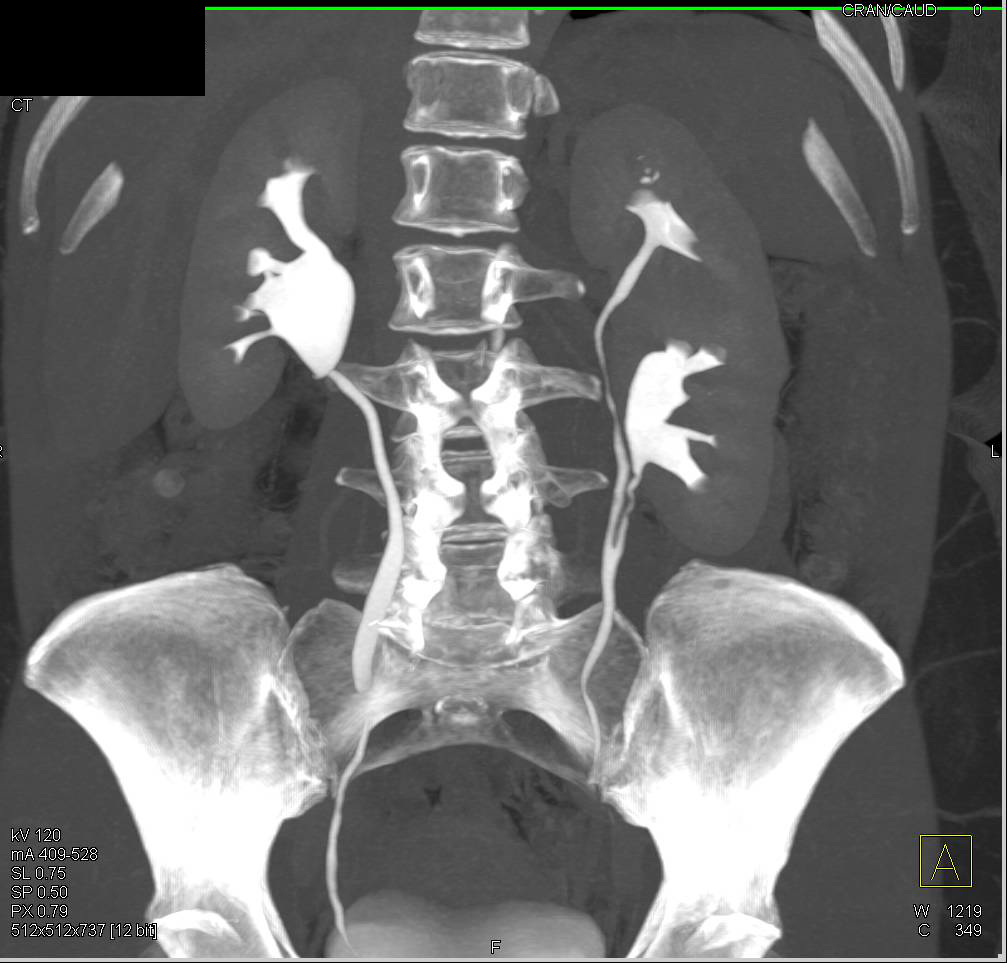
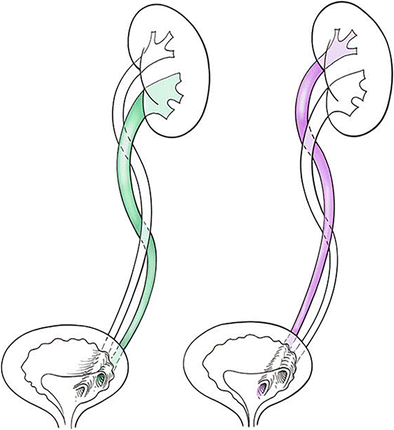
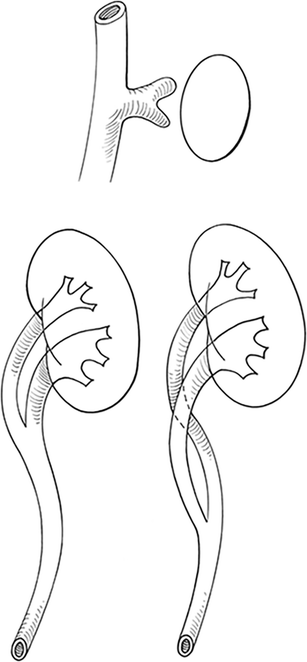
Duplicated left renal collecting system. A duplicated kidney also referred to as an ureteral duplication or duplicated collecting system means that a kidney has two ureters draining the kidney rather than the normal one. We describe a rare case of bilateral duplex collecting system with bilateral vesicoureteral reflux in which the refluxing ureter on the left side drains the upper pole moiety contrary to what is often found. Duplex kidneys can be uni- or bilateral and are more frequent in females.
The renal vein is an important landmark for this differential. With an obstructive process that resulted in chronic damage to the left upper pole collecting system and presents a difficult clinical scenario to manage. A calyceal diverticulum is a cyst-like lesion of the renal parenchyma but is differentiated from a true renal cyst by the presence of a communication with the renal collecting system.
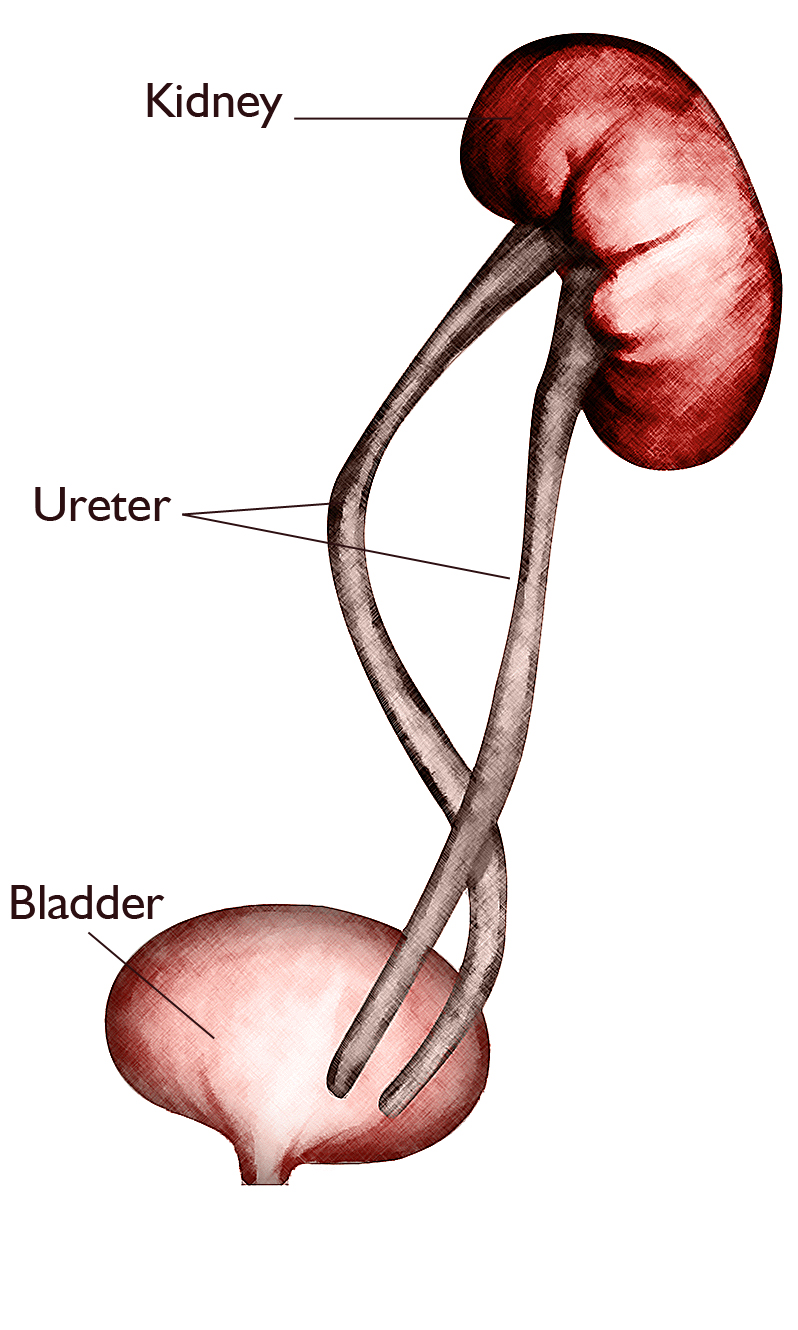
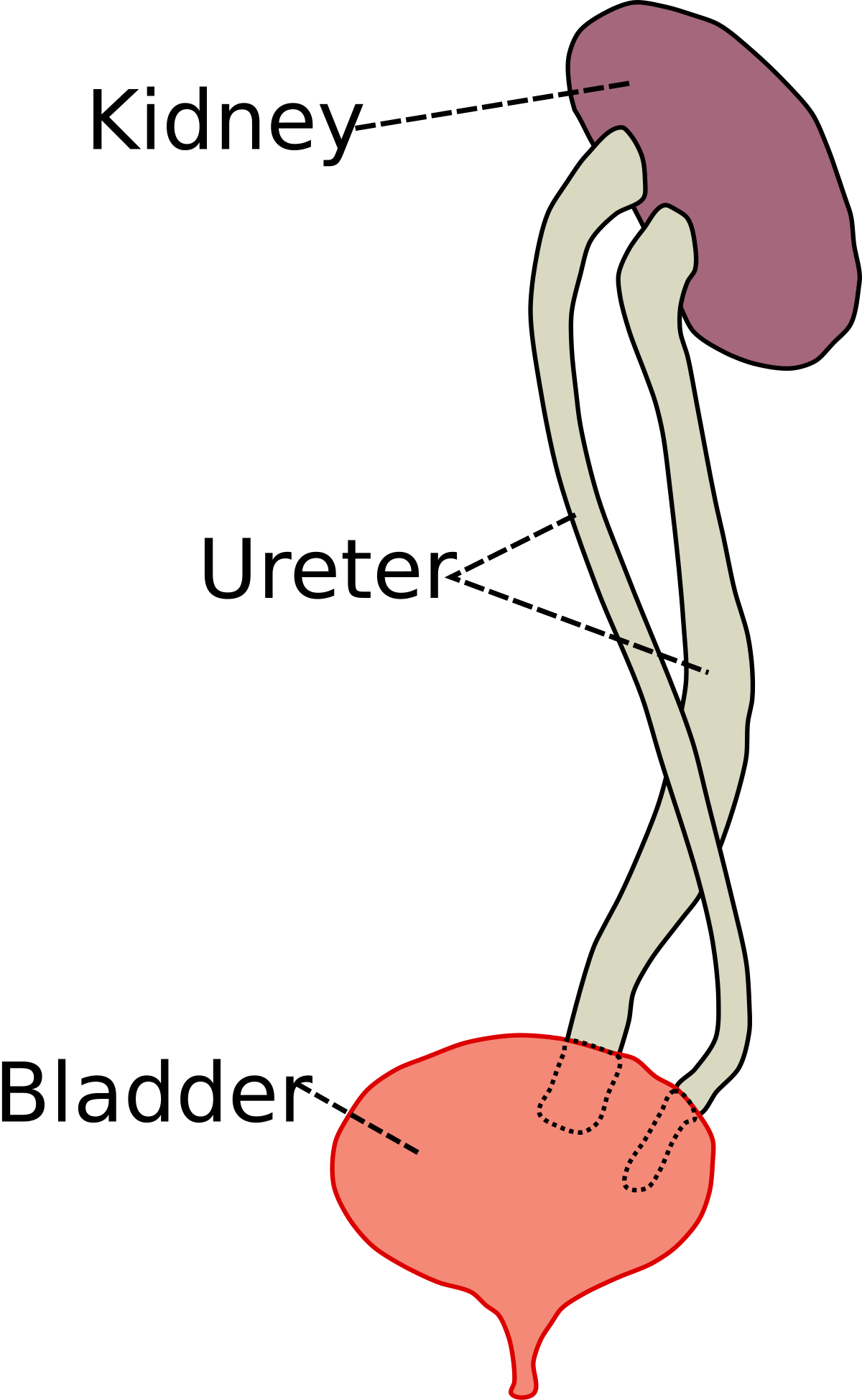
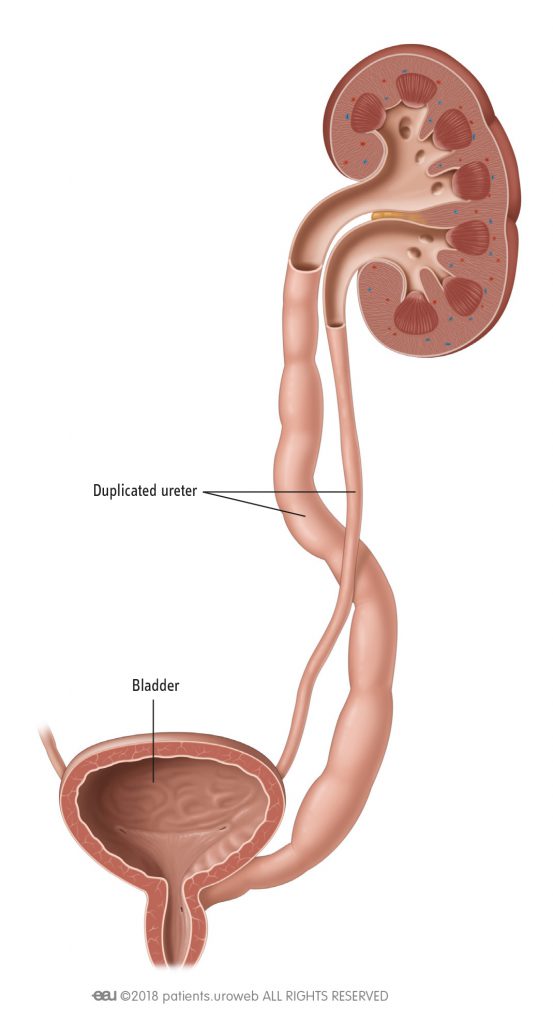
The two ureters may either drain the kidney into the bladder independently of one. Children with this condition often also have a ureterocele an enlargement of the portion of the ureter closest to the bladder due to the ureter. A consistent relationship of the duplicated ureters insertions into the bladder occurs in 85 of patients.
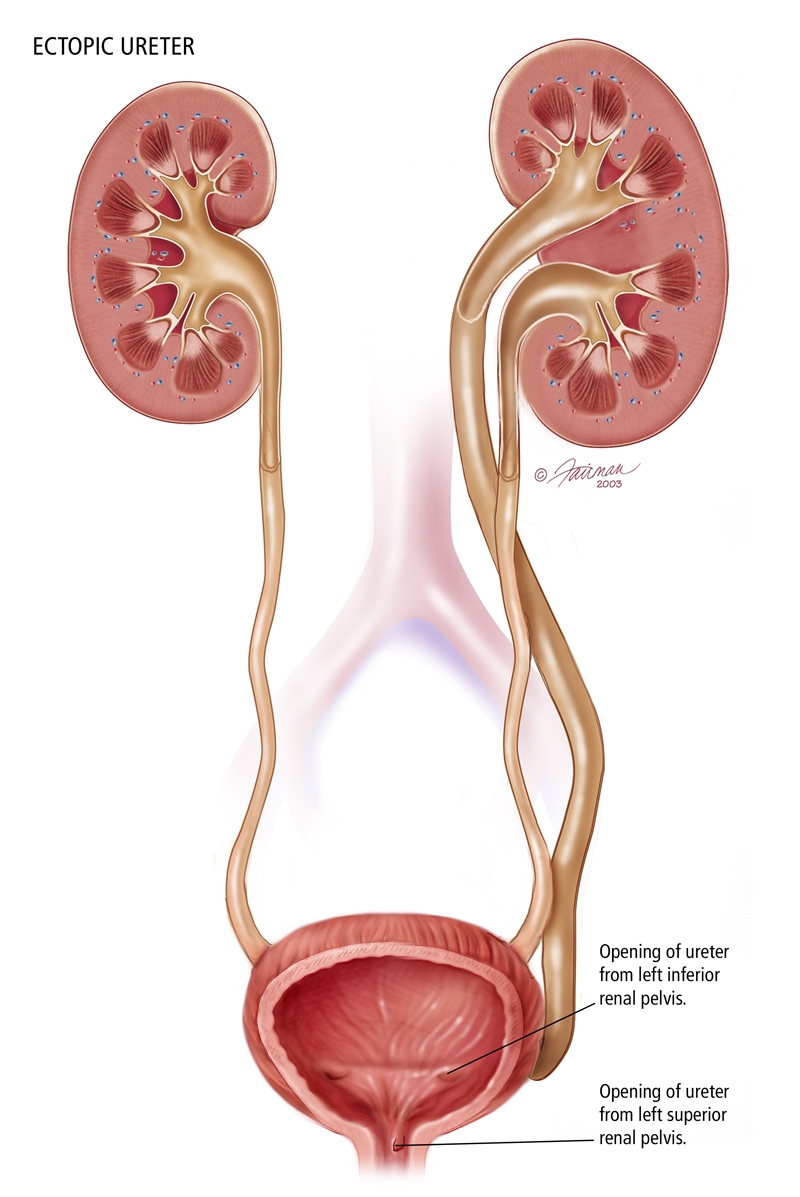
Duplicated Renal Collecting System With Ectopic Ureter in Female Bladder Exstrophy. Based on this finding we believe that the location where the duplicated ureter inserts. A single ureter is visualized below this point.
This occurs due to an incomplete fusion of the upper and lower pole of the kidney which creates two separate drainage systems from the kidney. 4000 pregnancies and is more frequent in females. A full-term newborn girl with a prenatal diagnosis of classic bladder exstrophy was found to have a complete duplicated left collecting system with.
Two ureters can be followed to the level of the mid pelvis. A duplicated ureter and urinary collecting system is a common anatomical anomaly that can be an asymptomatic normal variant or when abnormal can be associated with vesicoureteral reflux VUR incontinence ureterocele or obstructive uropathy as well as renal parenchymal scarring or dysplasia and decreased renal function. Ectopic ureters are commonly associated with a double duplex collecting system.
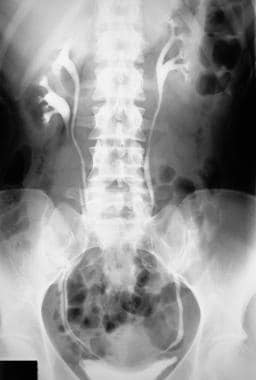
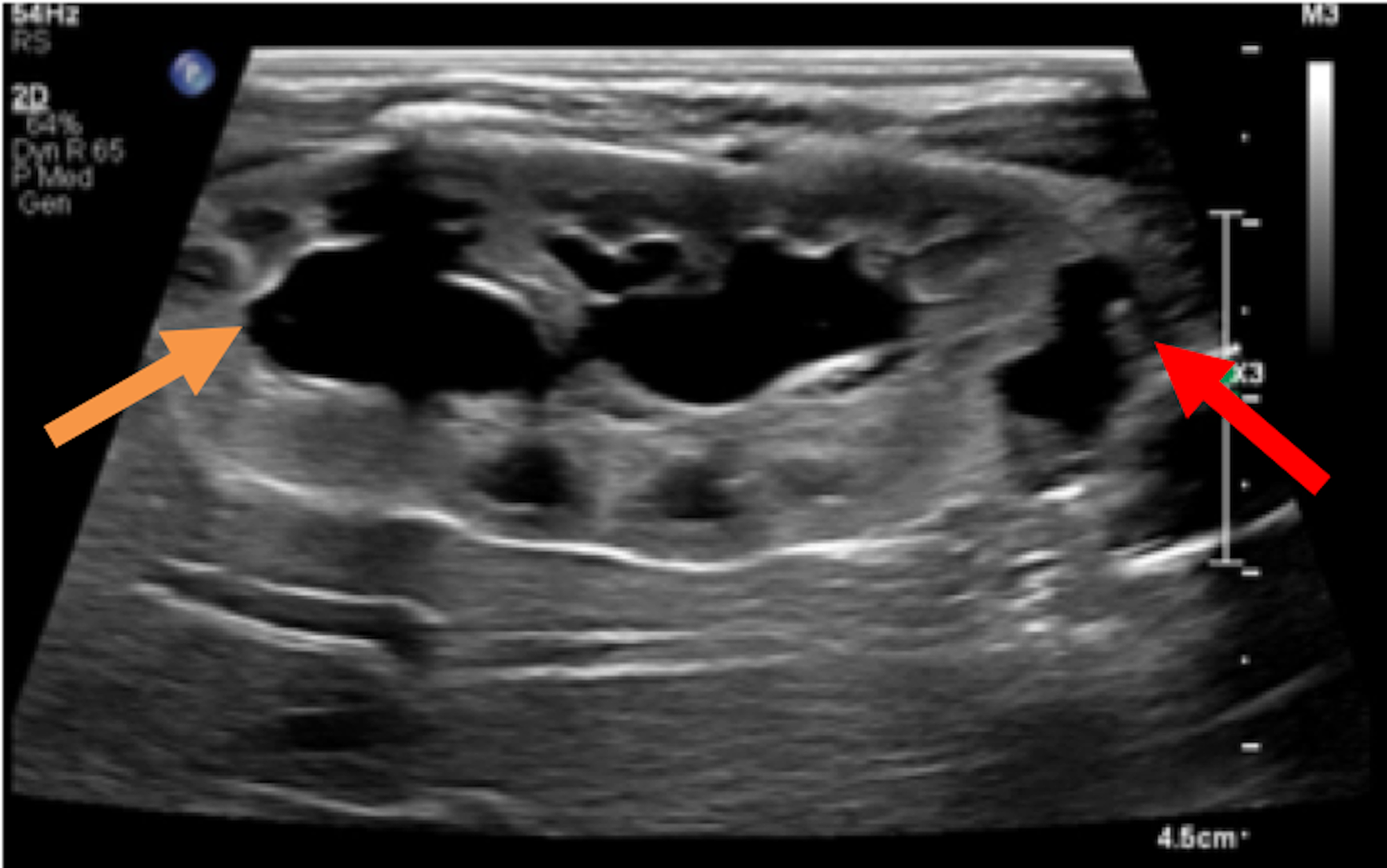
Ultrasound US may show dilatation of one or both renal pelves with an intervening band of renal tissue. In children with a duplex collecting system also known as ureteral duplication a kidney has two ureters tubes that carry urine from the kidney to the bladder rather than one.
The UVJ occurs in a normal position however a ureterocele is demonstrated at this point.
Q638 is a billablespecific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 4000 pregnancies and is more frequent in females. The upper pole moiety ureter inserts in a position inferior and medial to the lower pole moiety ureter. With an obstructive process that resulted in chronic damage to the left upper pole collecting system and presents a difficult clinical scenario to manage. Duplex kidney also known as duplicated ureters or duplicated collecting system is the most common birth defect related to the urinary tract. This occurs due to an incomplete fusion of the upper and lower pole of the kidney which creates two separate drainage systems from the kidney. Duplicated Renal Collecting System With Ectopic Ureter in Female Bladder Exstrophy. It is a common renal anomaly occurring with an incidence of 1 in 125 in the general population. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Q638 - other international versions of ICD-10 Q638 may differ.
A calyceal diverticulum is a cyst-like lesion of the renal parenchyma but is differentiated from a true renal cyst by the presence of a communication with the renal collecting system. A duplex kidney is characterised by the presence of two separate pelvicalyceal systems with complete or partial duplication of the ureters Fig. We describe a rare case of bilateral duplex collecting system with bilateral vesicoureteral reflux in which the refluxing ureter on the left side drains the upper pole moiety contrary to what is often found. Most calyceal diverticula are likely congenital in etiology while a minority may be sequelae of prior infection or stone disease Fig. A full-term newborn girl with a prenatal diagnosis of classic bladder exstrophy was found to have a complete duplicated left collecting system with. This may cause reflux or. It disproportionately affects the left kidney and is bilateral in 15 to 20 of cases.
































Post a Comment for "Duplicated Left Renal Collecting System"